The Science Behind Hyperpigmentation: Understanding Your Skin’s Dark Spots
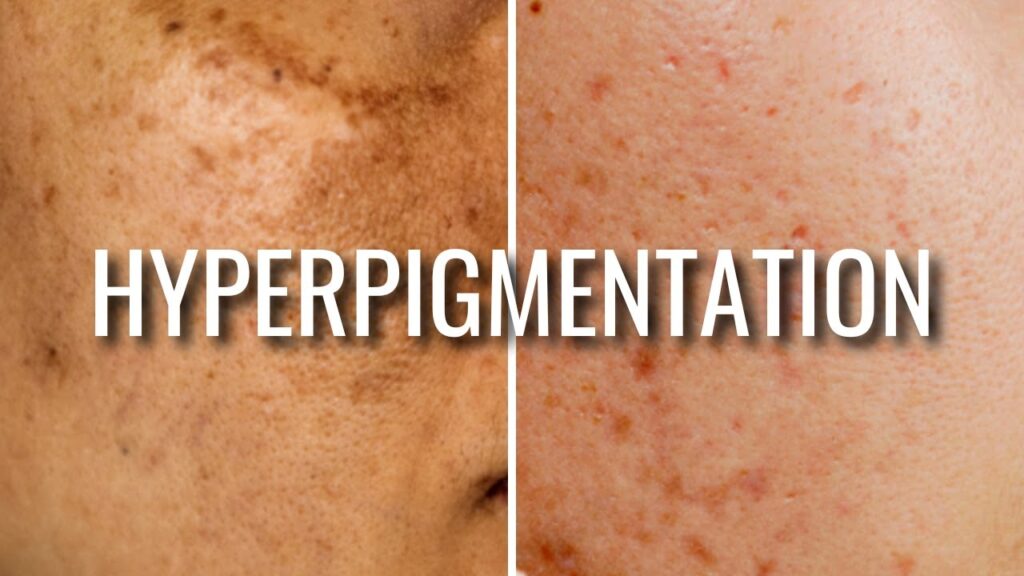
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the darkening of certain areas of the skin, resulting in uneven skin tone and patches. Understanding the science behind hyperpigmentation is crucial in order to effectively treat and prevent hyperpigmentation. As a professional author, I have delved deep into the topic of hyperpigmentation and its various aspects, and in this article, I will share my knowledge and personal experiences to shed light on this often misunderstood condition.

What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation refers to the excessive production of melanin, the pigment responsible for giving color to our skin, hair, and eyes. When there is an overproduction or uneven distribution of melanin, it leads to the formation of dark spots or patches on the skin. This can occur due to various factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, genetics, inflammation, and aging.
The effects of hyperpigmentation can be seen on different areas of the body, but it is most commonly found on the face, neck, hands, and arms. These areas are more prone to sun exposure and are therefore more susceptible to developing hyperpigmentation. Personally, I have struggled with hyperpigmentation on my cheeks for years, which has made me more passionate about understanding its causes and finding effective treatments.
Types of Hyperpigmentation
There are several types of hyperpigmentation, each with its own unique characteristics and causes. One common type is melasma, which is often triggered by hormonal changes such as pregnancy or the use of birth control pills. Melasma typically appears as brown or grayish patches on the face.
Another type is post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), which occurs as a result of skin inflammation or injury. This can be caused by acne breakouts, eczema flare-ups, or even harsh skincare treatments. PIH usually appears as dark spots or patches that fade over time.
Solar lentigines, commonly known as age spots or liver spots, are another form of hyperpigmentation. These are caused by long-term sun exposure and are more commonly found in older individuals. Age spots are typically small, flat, and brown in color.
Lastly, freckles are a type of hyperpigmentation that is often genetic. They are small, light brown spots that appear on the skin, especially on areas exposed to the sun. Freckles are more common in fair-skinned individuals and tend to darken with sun exposure.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
Understanding the causes of hyperpigmentation is essential in order to effectively prevent and treat this condition. While there can be multiple factors at play, genetics, hormones, sun exposure, skin inflammation, and age are some of the key contributors.
Genetics play a significant role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to hyperpigmentation. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to produce more melanin or have an uneven distribution of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin. Personally, I have noticed that many members of my family also struggle with hyperpigmentation, which suggests a genetic link. Skin lightening product reviews.
Hormonal changes can also trigger hyperpigmentation. Pregnancy, for example, often leads to the development of melasma due to the fluctuation of hormones. Similarly, certain hormonal conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can contribute to the formation of dark spots on the skin.
Sun exposure is a major factor in the development of hyperpigmentation. UV rays stimulate the production of melanin as a protective mechanism against sun damage. However, excessive sun exposure can lead to an overproduction of melanin, resulting in dark spots or patches on the skin. This is why it is crucial to protect our skin from the sun’s harmful rays by wearing sunscreen and seeking shade when necessary.
Skin inflammation, whether caused by acne, eczema, or other skin conditions, can also lead to hyperpigmentation. When the skin is inflamed, it triggers an increase in melanin production, which can result in dark spots or patches. Personally, I have experienced this firsthand when I had a severe acne breakout that left behind stubborn dark marks on my face.
Lastly, age plays a role in the development of hyperpigmentation. As we get older, our skin undergoes natural changes, including a decrease in collagen production and a slower cell turnover rate. These changes can lead to an accumulation of melanin and the formation of age spots or other types of hyperpigmentation.
Genetics and Hyperpigmentation
Genetics can significantly influence an individual’s susceptibility to hyperpigmentation. Some people may inherit genes that make them more prone to producing excessive melanin or having an uneven distribution of melanocytes. This can result in the development of hyperpigmentation even without external triggers such as sun exposure or hormonal changes.
There are also certain genetic conditions that are directly associated with hyperpigmentation. One example is albinism, a rare genetic disorder characterized by the absence or reduction of melanin production. Individuals with albinism often have very light skin and hair due to the lack of pigmentation. On the other hand, conditions like neurofibromatosis and Peutz-Jeghers syndrome can cause dark patches on the skin due to an overproduction of melanin.
Personally, I have always been curious about my family’s genetic background and how it may have influenced my own struggles with hyperpigmentation. While I don’t have any known genetic conditions related to pigmentation, it is clear that there is a genetic component at play considering the prevalence of hyperpigmentation among my relatives.
Hormones and Hyperpigmentation
Hormonal changes can have a significant impact on the skin’s pigmentation, leading to the development of hyperpigmentation. This is particularly evident in conditions such as melasma, which is often triggered by hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy or the use of hormonal contraceptives.
During pregnancy, the body experiences a surge in hormones, including estrogen and progesterone. These hormonal changes can stimulate the production of melanin, resulting in the formation of dark patches on the skin. This is commonly referred to as the “mask of pregnancy” or chloasma. Personally, I witnessed this firsthand when my sister developed melasma during her pregnancy. The dark patches on her face were a constant reminder of the hormonal changes her body was undergoing.
Hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, can also contribute to the development of hyperpigmentation. The synthetic hormones present in these medications can disrupt the natural balance of hormones in the body, leading to an increase in melanin production. This can result in the formation of dark spots or patches on the skin.
Sun Exposure and Hyperpigmentation
Sun exposure is one of the primary causes of hyperpigmentation. When our skin is exposed to UV rays from the sun, it triggers an increase in melanin production as a protective mechanism. Melanin acts as a natural sunscreen, absorbing and dispersing UV radiation to prevent damage to our DNA.
However, excessive sun exposure can lead to an overproduction of melanin, resulting in the formation of dark spots or patches on the skin. This is why individuals who spend a lot of time outdoors without proper sun protection are more prone to developing hyperpigmentation.
Personally, I have always been an avid lover of outdoor activities, whether it’s hiking, swimming, or simply enjoying a day at the beach. However, my love for the sun has come at a cost. Over the years, I have noticed an increase in hyperpigmentation on my face and arms, particularly on the areas that are most exposed to the sun. This has made me realize the importance of sun protection in preventing and minimizing hyperpigmentation.
Skin Inflammation and Hyperpigmentation
Skin inflammation can contribute to the development of hyperpigmentation. When the skin is inflamed, it triggers an increase in melanin production as part of the body’s natural defense mechanism. This can result in the formation of dark spots or patches on the affected areas.
Acne breakouts are a common cause of skin inflammation and subsequent hyperpigmentation. When a pimple forms, it causes inflammation in the surrounding skin, leading to an increase in melanin production. Even after the pimple has healed, it can leave behind a dark mark that takes time to fade.
Eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, can also contribute to hyperpigmentation. The constant inflammation and itching associated with eczema can disrupt the normal pigmentation process, resulting in the formation of dark patches on the affected areas.
Personally, I have struggled with acne breakouts throughout my teenage years and into adulthood. The aftermath of these breakouts has left behind stubborn dark marks on my face that take months to fade. This has made me more aware of the connection between skin inflammation and hyperpigmentation.
Age and Hyperpigmentation
As we age, our skin undergoes natural changes that can contribute to the development of hyperpigmentation. One of these changes is a decrease in collagen production, which leads to thinning and sagging of the skin. Thinner skin is more prone to damage and discoloration, making it easier for hyperpigmentation to occur.
Additionally, as we get older, our cell turnover rate slows down. This means that dead skin cells take longer to shed off, resulting in a buildup of melanin on the surface of the skin. This can lead to the formation of age spots or other types of hyperpigmentation.

Personally, I have noticed an increase in hyperpigmentation as I entered my thirties. The combination of sun exposure, hormonal changes, and the natural aging process has taken a toll on my skin. This has motivated me to explore various treatment options and preventive measures to minimize the appearance of hyperpigmentation.
How to Prevent Hyperpigmentation
Preventing hyperpigmentation is crucial in maintaining healthy and even-toned skin. While it may not always be possible to completely avoid hyperpigmentation, there are several steps that can be taken to minimize its occurrence.
First and foremost, sun protection is key in preventing hyperpigmentation. This includes wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade during peak sun hours, and wearing protective clothing such as hats and sunglasses. Personally, I have made it a habit to apply sunscreen every day, even when I’m indoors or on cloudy days. This simple step has made a noticeable difference in preventing new hyperpigmentation from forming.
Avoiding skin irritants is also important in preventing hyperpigmentation. Harsh skincare products, such as those containing alcohol or fragrances, can cause inflammation and trigger melanin production. Opting for gentle skincare products that are suitable for your skin type can help minimize the risk of developing hyperpigmentation.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is another crucial aspect of preventing hyperpigmentation. Eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants can help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals. Regular exercise improves blood circulation, which promotes healthy skin cell turnover. Getting enough sleep is also important as it allows the skin to repair and regenerate.
Treating Hyperpigmentation: Topical Treatments
There are various treatment options available for hyperpigmentation, ranging from topical creams to more advanced procedures. Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against hyperpigmentation and can be effective in fading dark spots or patches.
One of the most commonly used ingredients in topical treatments for hyperpigmentation is hydroquinone. Hydroquinone works by inhibiting the production of melanin, thereby lightening the skin. Other effective ingredients include kojic acid, azelaic acid, and retinoids, which help to exfoliate the skin and promote cell turnover. Meladerm cream real reviews.
Personally, I have tried several topical treatments for my hyperpigmentation, including creams containing hydroquinone and retinoids. While these treatments have helped to fade some of the dark marks on my face, they often require consistent and long-term use to see significant results.
Treating Hyperpigmentation: Laser and Light Therapies
For more stubborn or severe cases of hyperpigmentation, laser and light therapies can be effective treatment options. These procedures work by targeting the excess melanin in the skin and breaking it down, resulting in a more even skin tone.
One commonly used laser treatment for hyperpigmentation is the Q-switched laser. This laser emits high-intensity pulses of light that specifically target melanin without damaging the surrounding skin. Another popular option is intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy, which uses broad-spectrum light to target melanin and stimulate collagen production.
Personally, I have not undergone laser or light therapies for my hyperpigmentation as my condition is relatively mild. However, I have seen remarkable before-and-after photos of individuals who have undergone these treatments, which has piqued my interest in their effectiveness.
Chemical Peels for Hyperpigmentation
Chemical peels are another treatment option for hyperpigmentation that can help improve the appearance of dark spots or patches. During a chemical peel, a solution containing various acids is applied to the skin to exfoliate the top layers and promote cell turnover.
There are different types of chemical peels available, ranging from superficial peels to deeper peels. Superficial peels are milder and target the outermost layer of the skin, while deeper peels penetrate deeper into the skin to target more severe hyperpigmentation.
Chemical peels can be effective in reducing hyperpigmentation, but they may require multiple sessions to achieve desired results. Personally, I have not undergone a chemical peel for my hyperpigmentation, but I have considered it as a potential treatment option in the future.
Home Remedies for Hyperpigmentation
In addition to professional treatments, there are also several home remedies that are often touted as natural solutions for hyperpigmentation. These remedies typically involve the use of ingredients commonly found in the kitchen or pantry, such as lemon juice, apple cider vinegar, and aloe vera.
While some individuals claim to have had success with these home remedies, it is important to approach them with caution. Natural ingredients can be potent and may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals. It is always best to consult with a dermatologist before trying any home remedies for hyperpigmentation.
Personally, I have experimented with a few home remedies for my hyperpigmentation, including applying lemon juice to my dark spots. While I did notice a slight improvement in the appearance of my hyperpigmentation, I also experienced some skin irritation. This made me realize the importance of seeking professional advice before trying any DIY treatments.
In conclusion, hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that affects many individuals worldwide. Understanding the science behind hyperpigmentation is crucial in order to effectively prevent and treat this condition. By knowing the causes and triggers of hyperpigmentation, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their skin from further damage. This may include wearing sunscreen daily, avoiding excessive sun exposure, and using skincare products that target hyperpigmentation. Additionally, seeking professional help from dermatologists or estheticians can provide personalized treatment options such as chemical peels, laser therapy, or topical creams. It is important to remember that hyperpigmentation is a complex condition and may require a combination of treatments for optimal results. With proper care and treatment, individuals can regain confidence in their skin and achieve a more even complexion.